
Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM) service
What is CBAM
CBAM (Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism), commonly known as "carbon border tax", is a new policy officially implemented in October 2023. The European Union imposes taxes on the carbon emissions of certain imported goods.
Currently, CBAM covers a range of products, including cement, aluminum, fertilizers, iron and steel, chemicals (hydrogen), and electricity. The specific determination of whether a product exported to the EU falls under CBAM can be based on the CN code list published by the European Union.
Carbon Newture helps companies with CBAM reporting and provides additional supportive services.

CBAM requirements
Transitional period -1 October 2023 to 31 December 2025
Reporting requirements:Within one month after the end of each quarter, submit a quarterly CBAM report (Note: From July 2024 onwards, it is not permissible to use default values for estimating carbon emissions).
Tax payment requirements:No CBAM taxes need to be paid. However, failure to declare on time or incomplete reporting may result in penalties ranging from 10 to 50 €/tonne of carbon emissions.
Definitive period - starting on 1 January 2026
Reporting requirements:Before May 31 of each year, submit the CBAM report for the previous calendar year (Verified and accompanied by a verification report from the verification body).
Tax payment requirements:CBAM taxes must be paid, calculated as follows.
How CBAM taxes are calculated
The calculation of CBAM taxes typically involves multiplying the tax rate by the total carbon emissions of the product. For detailed information on tax rates and carbon emissions calculations, please refer to the diagram on the right and the accompanying notes.

Challenges you may face
Difficult reporting
Numerous forms in English, complex carbon calculations, and challenging professional terminology.
High costs
Gathering extensive data requires significant time and labor costs.
Data gaps
Missing activity level data and difficulty in determining activity factors.
Risk
Reporting inaccurately can lead to additional tax burdens as it directly relates to future CBAM tax payments.
What we provide
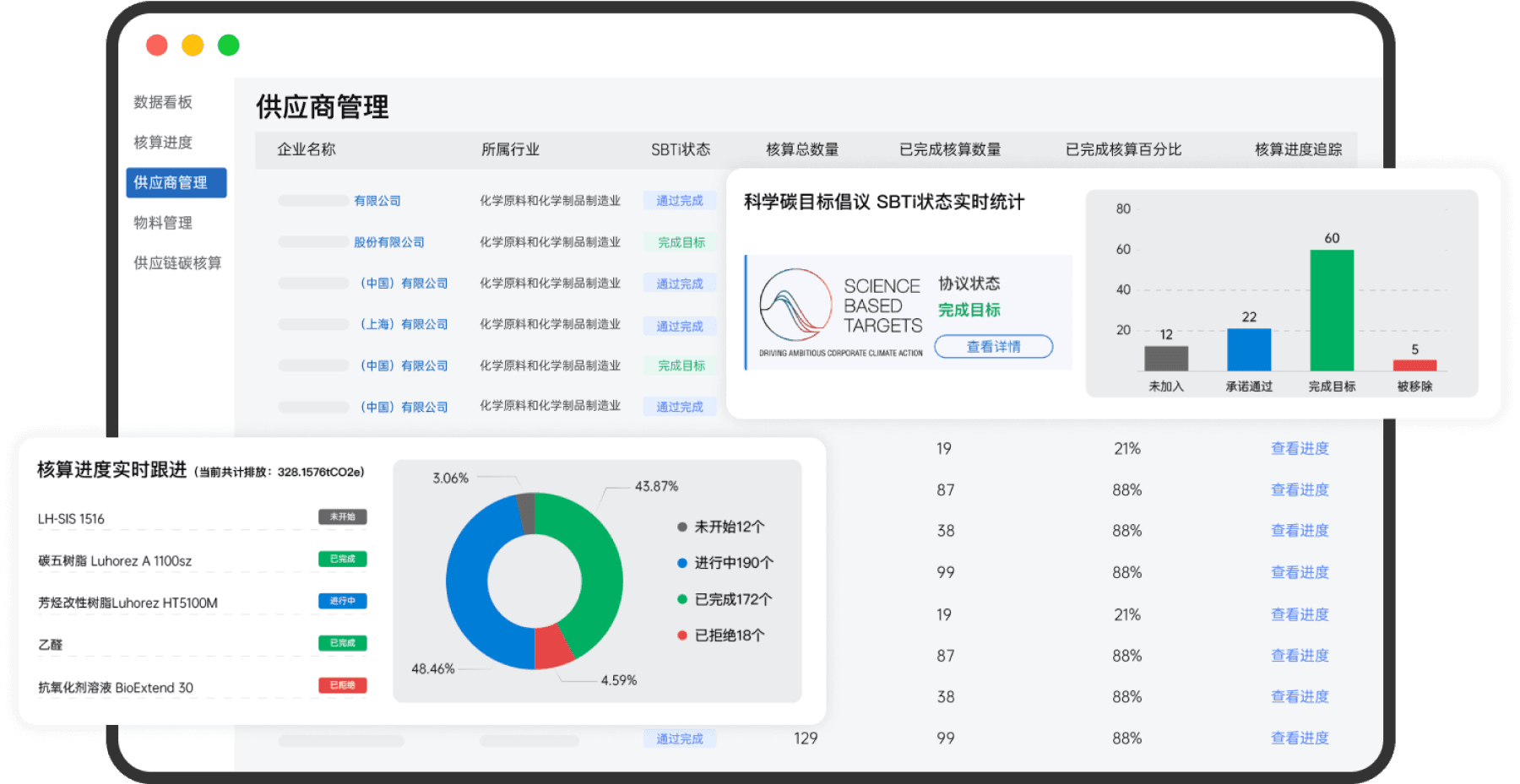
Supply Chain Management Platform: Assisting with internal data collection and upstream data communication
Establishing a carbon emission database to effectively mitigate risks arising from the lack of data (such as high CBAM taxes due to using only estimated values in the absence of actual data).
Helping you efficiently manage carbon data within the enterprise, bridging the gap in supply chain carbon data and overcoming trade barriers.
Actively address green trade barriers to ensure the secure and compliant flow of carbon data
Complete CBAM reporting with actual values to avoid fines for non-compliance or additional carbon taxes due to the use of inappropriate estimation values.
Assist you in building a CBAM carbon database to achieve compliant and efficient CBAM reporting.

Our advantages
Cost-Effectiveness
Efficiency
Authority
Standards we follow

Environmental management — Life cycle assessment — Principles and framework

Environmental management - Life cycle assessment - Requirements and guidelines

Greenhouse gases - Carbon footprint of products - Requirements and guidelines for quantification

Greenhouse gases: Specification with guidance at the organization or project level for quantification and reporting of greenhouse gas emissions and removals

Requirements and Guidelines for Quantifying the Carbon Footprint of Products in Terms of Greenhouse Gas Emissions

General guideline of the greenhouse gas emissions accounting and reporting for industrial enterprises

Requirements of the greenhouse gas emission accounting and reporting—Part 7: Flat glass enterprise

Requirements of the greenhouse gas emissions accounting and reporting —Part 10: Chemical production enterprise

Requirements of the greenhouse gas emissions accounting and reporting—Part 12:Textile and garment enterprise
Empower brands to enhance their green value
helping enterprises successfully create ”Carbon Neutrality“ IP and a new brand image

Business services industry
Shanghai Foreign Trade (Pudong): Obtains TÜV SÜD conformity assessment report

